Do you know that your liver has an important role in maintaining the natural color of your skin? If it is not functioning well, it will give you certain telltale signs. One of these signs is a yellow skin tone.
If your skin is turning yellow, this could be a sign of jaundice. The yellow color of jaundice is caused by a buildup of bilirubin, a waste byproduct of aging red blood cells.
When there is excess bilirubin in your system, your skin will manifest a yellow or pale skin tone. There are many underlying conditions that can cause bilirubin to build up in your system.
In severe cases, the whites of the eyes may also turn orange or brown. The color of the urine may also turn dark, and the stools may turn pale.
Another possible reason for the yellow skin color could be carotenemia. Carotenemia is caused by too much vitamin A – from yellow or orange-colored foods such as carrots, sweet potatoes, or squash.
A yellow skin tone could also be caused by anemia.
Read on to learn more about yellow skin tone, including its possible causes and treatments.
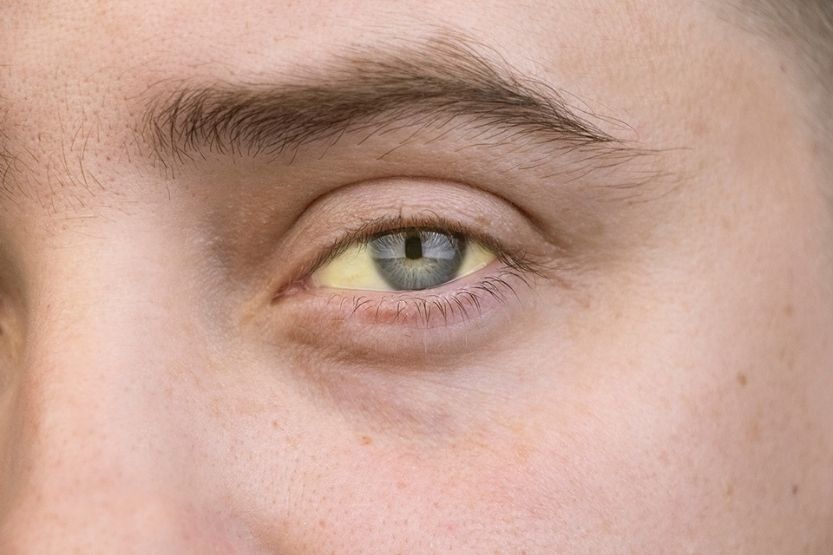
What Does It Mean When You Have Yellow Skin Tone?
If your skin is yellow, you may have a skin condition called jaundice. This is not actually a disease but is a symptom of an underlying condition.
The yellow skin color is due to a buildup of bilirubin in your system. There are many causes for the buildup of bilirubin in your body.
One possible cause of yellow skin tone could be the excess intake of vitamin A. If the foods that you eat are rich in vitamin A such as carrots and squash, it will manifest in the yellow-orange coloring of your skin, mostly in the palms of your hands and at the soles of your feet.
This condition is referred to as carotenemia. If you have this condition, the beta-carotene levels in your blood will be overly high. This is caused by excessive vitamin A-rich foods such as carrots, sweet potatoes, and squash.
Another reason for a yellow skin tone is if your body cannot correctly process and get enough oxygen. Thus, you will easily get tired and feel lethargic. Your skin will also turn pale and yellowish.
Anemia can also cause your skin to turn pale or yellowish. This condition can be caused by iron deficiency and is typically related to decreased oxygen delivery to your entire body.
Shortness of breath, lack of energy, unexplained fatigue, and chest pain during physical activity are just some of the symptoms.
Jaundice is also common with newborns, especially those who are prematurely born. Excess bilirubin develops in premature babies because their livers are not yet fully developed. They call this condition breast milk jaundice.
Symptoms of Jaundice
While yellow-tinted skin and yellowish eyes are the most common jaundice characteristic, there are more severe cases wherein the white area of the eyes will also turn orange or brown. The urine may also grow darker, and the stools may grow pale.
Jaundice is just a manifestation of an underlying health condition. This condition could be viral hepatitis or some other disease. You may experience other symptoms, such as vomiting and excessive fatigue. It is effortless to misdiagnose the cause of yellow skin color.
If your only symptom is your skin’s yellowing, then it could probably be only due to your excessive intake of vitamin A-rich foods.
This causes the overabundance of the anti-oxidant beta carotene in your system. Beta-carotene comes from sweet potatoes, carrots, squash, and pumpkins.
Causes of Jaundice
Small amounts of red blood cells die inside your body every day. Your body also replaces them with new ones. Your liver removes the dead red blood cells and, in the process, creates bilirubin. It also breaks down this bilirubin so the body can remove it through your stool.
The problem of jaundice shows up if there is too much bilirubin in your system. This skin condition will manifest due to the following conditions:
- There is a huge amount of red blood cells breaking down or dying and going to your liver;
- You have a damaged liver. Thus, it cannot function well; and
- Bilirubin from your liver cannot be transported to your digestive tract and unable to be turned into the stool.
Jaundice is usually a manifestation of a problem in the liver, pancreas, or gallbladder. The causative factors of jaundice include the following:
- Cancer of the liver, pancreas, or bile ducts
- Viral infections
- Blood disorders, congenital disabilities, gallstones, and other medical conditions
- Intake of certain medications or drugs
The section below is a more detailed description of the internal conditions that can cause the yellowing of your skin:
Other Possible Causes of Yellow Skin
1. Hepatitis
It can be chronic or acute hepatitis, depending on what causes the condition. Hepatitis can also be due to an inflammatory condition due to the following:
- Autoimmune disease,
- Toxins, medications,
- Alcohol,
- Severe blood loss,
- Drugs, or
- Plain viral infection.
Possible symptoms include yellow skin tone or eyes, loss of appetite, fluid buildup in the abdomen, nausea, vomiting, pain in the right upper abdomen, and itching skin
2. Hepatitis A
This liver condition is due to a hepatitis A infection. It is highly contagious and can spread through water and food contamination. Hepatitis A has no long-term effects and is not that serious. Immunization can prevent it from spreading.
Usual symptoms include abdominal pain, loss of appetite, vomiting, nausea, and body pains. After a week of having the infection, your liver will enlarge, and you may experience itchy skin, yellow skin tone, and eyes. You will also notice your stools getting pale and your urine getting dark.
3. Hepatitis B
The hepatitis B virus can infect you through direct contact with infected blood. Here are the possible modes of transmission of this virus:
- Vaginal, oral, and anal sex without any protection;
- Using infected personal items;
- Sharing contaminated needles; and
- Possible transmission from the infected mother to baby.

The typical symptoms include muscle pain, fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, joint and muscle pain, abdominal discomfort, dark urine, yellowing of the whites of the eye, and yellow skin tone.
Hepatitis B can cause complications, including liver cancer, cirrhosis of the liver, liver failure, and death. With regular immunization, you can protect yourself from hepatitis B.
4. Hepatitis C
Transmission of this virus is possible through blood-to-blood contact with a person infected with HCV. Symptoms can be mild to severe and include loss of appetite, joint pain, dark urine, abdominal discomfort or pain, fever, and jaundice.
About 70 to 80% of those infected with the hepatitis C virus don’t show any symptoms.
5. Hepatitis E
This is a potentially serious liver disease. The hepatitis E virus can spread through the following:
- Blood transfusions,
- Eating and drinking contaminated food and water, and
- From mother to child.
The majority of the cases are resolved after a couple of weeks. While other cases result in liver failure.
This condition’s symptoms are loss of appetite, liver enlargement, joint pain, abdominal pain, dark urine, fever, vomiting, nausea, and fatigue.
6. Hepatitis D
This virus causes liver inflammation. You can only contract this disease if you are infected with the hepatitis B virus.
This condition is contagious and can spread by direct contact with the body fluids of the infected individual. Some of the symptoms include abdominal pain, loss of appetite, joint pain, vomiting, fatigue, dark urine, and yellow skin color.
7. Yellow Fever
Mosquitoes spread this disease. It’s like the flu and is potentially lethal. It is most common in South America and Africa.
If you plan to go to areas wherein this disease is quite common, make sure you get yourself vaccinated.
Beginning symptoms are similar to influenza virus infection, including fever, headache, chills, loss of appetite, and body aches. At its toxic phase, the initial symptoms may fade in about 24 hours but return with a vengeance.
These symptoms may include vomiting, seizures, heart rhythm problems, bleeding from the eyes, nose, mouth, delirium, and decreased urination.
8. Alcoholic Liver Disease
As the name suggests, this is due to heavy drinking of alcohol over a long period of time. The symptoms vary depending on the degree of damage that the liver has sustained.
Some of the common symptoms include easy bruising and bleeding, swelling, and pain in the abdomen, vomiting, nausea, mental condition changes, weight loss, fatigue, and jaundice.
9. Liver Cancer
This condition is a consequence of the liver cells going out of control and becoming cancerous. Different types of primary liver cancer originate from the different liver cells that constitute the liver.
This condition’s symptoms include tenderness in the upper right abdomen, pain and abdominal discomfort, nausea and vomiting, white and chalky stools, fatigue, easy bruising and bleeding, yellow skin tone, and eyes.
10. Drug-Induced Immune Hemolytic Anemia
This condition happens when upon intake of a certain medication, the body’s immune system attacks the red blood cells. The initial symptoms may show up in minutes after taking the medication. Some symptoms may manifest after a few days.
These symptoms include dark urine, rapid heart rate, fatigue, shortness of breath, pale skin, pale gums, and yellow skin tone.
11. Acute Pancreatitis
This is a medical emergency condition that requires immediate medical care. It is a painful inflammation of the pancreas. This condition is typically due to alcohol abuse and gallstones.
Some symptoms include a sudden and then constant intense pain felt in the abdomen’s upper part. The pain may travel all over the body, including the back. Pain gets worse when lying on your back. Pain is relieved when sitting or leaning forward. Vomiting and nausea can happen.
12. Sickle Cell Anemia
This is a red blood cell genetic disease that causes red blood cells to take on the shape of a sickle or a crescent moon. As a result, the infected cells can get trap in small vessels. This causes blocks of blood from getting to the different parts of your body.
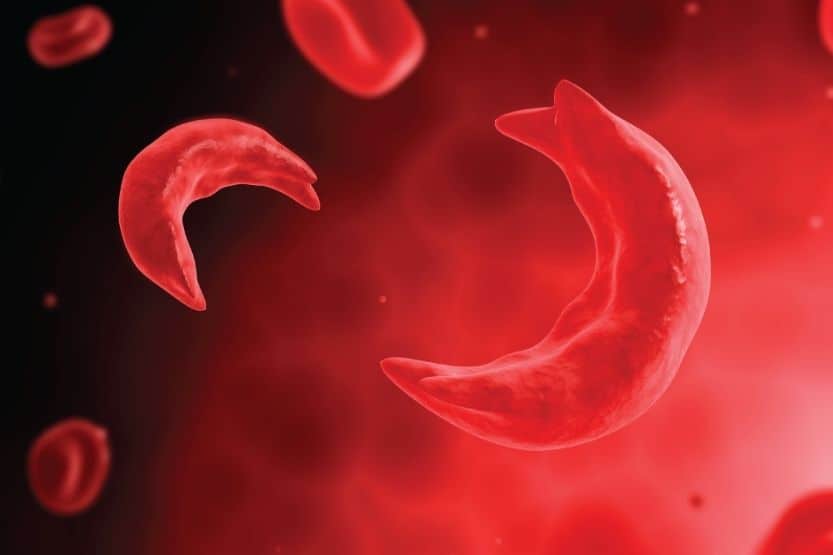
Due to their abnormal shape, they degenerate faster than normal ones. This leads to anemia. Some of the symptoms include pale skin and gums, swelling in the hands and feet, excessive fatigue, severe pain in the arms, legs, back, chest, frequent infections, and yellow skin tone.
13. Bile Duct Obstruction
This condition is a medical emergency that requires urgent attention. Some causes include gallstones but can also be due to gallbladder or liver damage, cysts, tumors, and inflammation.
Symptoms can include itchy skin without rashes, dark urine, pale stool, pain in the upper right side of the abdomen, fever, nausea, and vomiting, and yellowish skin tone.
What does it mean when you have a yellow skin tone? Yellow skin tone or color usually indicates that you have a medical condition called jaundice. This condition is due to the bilirubin build-up in your body. Birubilin refers to the yellowish byproduct after the breakdown of red blood cells.
Next, let’s look at possible treatments and solutions for jaundice and yellow skin tone.
Treatments and Solutions
Treatment for jaundice largely depends on the cause of the condition. Remember that jaundice is not really a disease but a skin condition that manifests because of an underlying cause or condition in your system.
When you ask the help of a medical provider, they will treat your jaundice and not the symptom itself. If you follow his advice, you will begin to see the color of your skin returning to normal.
If jaundice is present in newborn babies, you can expect it to disappear after 1 to 2 weeks, says the American Liver Foundation. Moderate jaundice in adults does not require treatment.
According to experts, jaundice treatment in infants can be done in the home or a hospital using phototherapy. This procedure is designed to remove excess bilirubin.
Phototherapy makes use of light waves. The body then absorbs these waves through the skin and blood. These light waves help your body to change the excess bilirubin into waste products that can be removed.
In phototherapy, a light pad is typically used. It simulates natural sunlight. This pad is placed on the skin during treatment.
One side effect of this therapy is frequent bowel movements with stools that are greenish in color. These waste matters are actually bilirubin being removed from your body. In severe cases, bilirubin is removed using blood transfusion.
How to Prevent Jaundice?
If your jaundice is originated from eating vitamin A-rich foods, the best thing you can do is avoid eating carrots, squash, sweet potatoes, pumpkins, and other similar foods.
Once your bilirubin levels become normal, the yellow skin color should fade away. The normal color of your skin will be restored.
However, if you have avoided these foods and your skin still looks jaundiced, there could be an underlying cause.
You should, therefore, consult your medical provider to determine the real cause of your skin condition. They could be one or two of the causes I have discussed above. Your health provider should know the proper procedure to resolve your condition.
Conclusion: Yellow Skin Color and Tone
A yellow skin tone can be a sign of jaundice. Jaundice is caused by a buildup of bilirubin, a waste byproduct of aging red blood cells.
When bilirubin builds up in your system, your skin will manifest a yellow or pale skin tone. There are many underlying conditions for the bilirubin buildup in your system. Some of these conditions include hepatitis, alcohol-induced live damage, liver cancer, yellow fever, among others.
The key to avoiding jaundice or a yellow skin tone is to have a healthy and balanced lifestyle.

![Bleeding Pore on Nose [11 Possible Causes and Treatments] bleeding pore on nose](https://skincaregeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/04/bleeding-pore-on-nose-150x150.jpg)
![Bruise Itches [Causes and Treatments for an Itchy Bruise] bruise itches](https://skincaregeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/04/bruise-itches-150x150.jpg)

![Golden Brown Skin Tone - What Is It? [With Pictures] golden brown skin](https://skincaregeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/04/golden-brown-skin-150x150.jpg)
![Neutral Skin Tone Defined [and Best Colors for Neutral Skin] neutral skin tone](https://skincaregeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/neutral-skin-tone-150x150.png)



