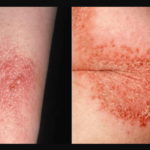
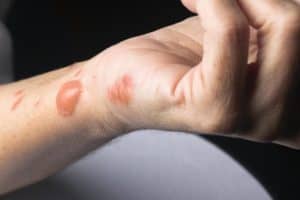
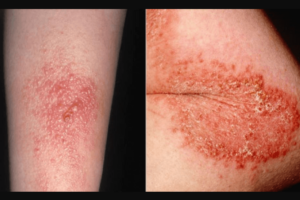
Yellow spots on the skin are a symptom of many possible medical conditions, ranging from mild to severe. For this reason, it’s essential to rule out and confirm the root cause to find the right treatments. In this article, you’ll learn some of the possible causes and treatments for yellow spots on the skin.
What are yellow spots on skin? Yellow spots on the skin or yellowish skin is often a medical condition called jaundice. Liver diseases, hypothyroidism, and bile duct blockage are just a few underlying issues that may cause jaundice.
Depending on the underlying condition, possible treatments of yellow skin (caused by jaundice) may include topical creams, laser treatment, and chemical peels, among others.
11 possible causes for yellow spots on skin are as follows (the first four on the list are the most common causes):
- Hepatitis
- Alcoholic Liver Disease
- Bile Duct Blockage
- Adverse Reactions from Drugs or Medicinal Herbs
- Atopic Eczema
- Skin Injuries
- Hormonal Imbalances
- Kidney Disease
- Malaria
- Pancreatic Cancer
- Infectious Mononucleosis
8 possible natural treatments for yellow spots on skin are as follows:
- Eat Iron-Packed Foods
- Drink 2-4 Cups of Coffee Daily
- Start Eating Papaya
- Shed the Extra Pounds
- Add Fiber-Rich Foods to Your Diet
- Stop Drinking Alcohol
- Try Spices and Herbs
- Get Adequate Rest
Read on to learn more about yellow spots on skin, including the possible causes and treatments. First, I’ll list some common health problems that show a yellowish discoloration of the skin.
Most Common Causes of Yellow Spots on Skin
The most common cause of yellow spots on the skin is jaundice. Jaundice commonly affects recently born babies, but it could also affect adults. This condition is characterized by a yellowish discoloration of the skin and sclera (whites of the eyes).
A person experiences jaundice because of an increased level of bilirubin in the blood (hyperbilirubinemia). This yellowish-orange pigment is a by-product of hemoglobin breakdown. Hemoglobin is a red-colored protein that carries oxygen in the blood.
Bilirubin, when transported to the liver, combines with bile, which is a greenish-yellow liquid produced by the liver. Under normal circumstances, the body eliminates bilirubin through bowel movements and a small amount through the urine.
If the body can’t get rid of it fast enough, it accumulates in the blood and is eventually deposited in the skin.
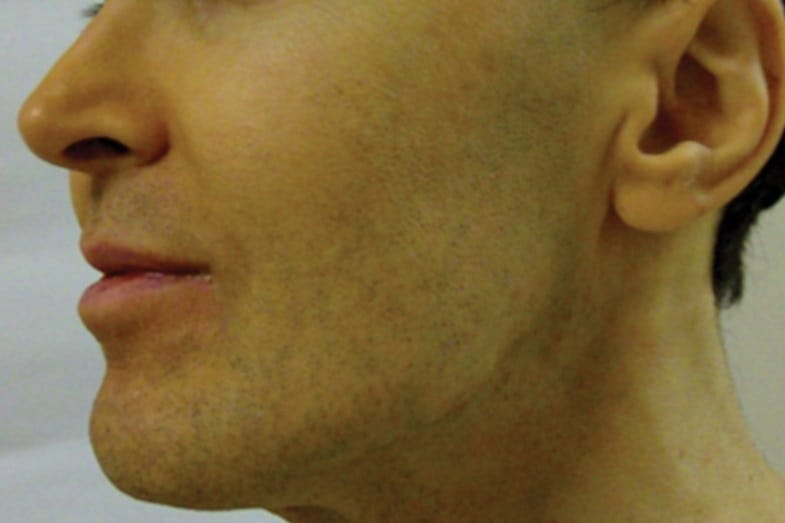
Many medical conditions can cause jaundice (yellow spots on skin or yellow discoloration). Four of the most common causes are:
- Hepatitis
- Alcoholic Liver Disease
- Bile Duct Blockage
- Adverse Reactions from Drugs or Medicinal Herbs
1. Hepatitis
Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver, often caused by a viral infection. There are five types of viral hepatitis: A, B, C, D, and E.
The virus spreads from person to person through direct contact with an infected person’s blood or body fluids. Sharing a razor or a toothbrush is another way to catch the disease. In the U.S., people often get it through unprotected sexual intercourse.
2. Alcoholic Liver Disease
Alcoholic liver disease, also called as alcohol-related liver disease (ARLD), is caused by drinking too much alcohol. This condition causes inflammation, scarring, and buildup of excess fat in the liver.
The signs and symptoms of this disease include extreme tiredness, digestive problems, and yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes.
This disease can become severe when it leads to liver failure. However, depending on the extent of liver damage, some cases respond well to treatment.
3. Bile Duct Blockage
Gallstones usually affect 20-25 million adults in the United States. [1] And around 15 percent of those people with gallstones will develop bile duct blockage. When that happens, it could result in an inflamed gallbladder or cholecystitis in medical terms.
One of the typical symptoms of cholecystitis is the yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes. However, this condition is usually mild.
4. Adverse Reactions from Drugs or Medicinal Herbs
There are different ways medical drugs or herbal medicines could cause liver disease. For instance, some drugs are chemically changed by the liver into substances that could indirectly or directly damage the liver. Other drugs are directly toxic to the liver only when taken in excessive amounts.
Drugs that are harmful to the liver include:
- Acetaminophen (Tylenol)
- Amoxicillin-clavulanic acid
- Azithromycin
- Captopril
- Chlorpromazine
- Cimetidine
- Ciprofloxacin
- Dicloxacillin
- Erythromycin
- Naproxen
- Ofloxacin
- Phenytoin
Other Causes of Yellow Spots on Skin
Medical conditions and drug reactions that damage the liver aren’t the only causes for yellow spots on the skin. Here are other causes for yellow spots on the skin that are less common but still possible:
Less common causes of yellow skin discoloration are as follows:
- Atopic Eczema
- Skin Injuries
- Hormonal Imbalances
- Kidney Disease
- Malaria
- Pancreatic Cancer
- Infectious Mononucleosis
1. Atopic Eczema
Atopic eczema is a group of diseases that makes the skin overly dry, swollen, red, and itchy. It usually happens as a response to allergens (e.g., pet dander and pollen), chemicals (from soaps and household cleaners), dry skin, stress, and infection.
In some cases, this skin condition could lead to an infection. When there’s an infection, the affected area of the skin becomes swollen and sore. The formation of yellow crusts or yellow-white spots on the skin can also occur.
2. Skin Injuries
Bruises, burns, and wounds are just some of the common types of skin injuries. It’s considered normal for some of these skin injuries to become yellowish over time as they heal slowly. The yellow discoloration of the affected area happens when biliverdin, a green bile pigment, breaks down and creates bilirubin.
3. Hormonal Imbalances
Thyroid disorders, in particular, are known for their wide-ranging effects on the skin, hair, and nails. When the thyroid gland secretes fewer hormones (hypothyroidism), the skin becomes thick, dry, rough, and scaly. The hands and feet also turn yellowish. When it secretes a lot of hormones (hyperthyroidism), the skin becomes sweaty, red, swollen, and jaundiced.
4. Kidney Disease
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a medical condition wherein the kidneys slowly lose their ability to filter waste products (e.g., salts, urea, and phosphates) and excess fluids from the blood. For countries in the West, the usual suspects for this disease are diabetes and hypertension (high blood pressure). [2]
People with CKD may have yellowish-brown skin. If their blood urea (a nitrogen-containing compound) is high, a white and powdery substance will be left on their skin.
5. Malaria
Malaria is a life-threatening mosquito-borne disease that affects around 2,000 Americans every year. [3] Most of these cases include people traveling from countries where malaria transmission is intense.
The hallmark symptom of malaria is fever (as high as 107ºF or 41.7ºC), which could be accompanied by muscle pain, shaking, and shivering. Infected people suffer from anemia and jaundice as a result of the destruction of red blood cells.
6. Pancreatic Cancer
One of the main functions of the pancreas is to convert the food you eat into energy for the body’s cells. It plays a key role in regulating blood sugar.
According to Cancer.Net, African-Americans are more likely to develop pancreatic cancer than white people.
They have also estimated that around 56,770 American adults were expected to be diagnosed with this type of cancer in 2019. [4] It’s common for pancreatic cancer patients to have jaundice due to blockage of the bile ducts.
7. Infectious Mononucleosis
Infectious mononucleosis, or mono, in short, is caused by the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). The virus jumps from person to person through saliva. That’s why mono is often called the “kissing disease.”
Additionally, mono can cause hepatitis, which also causes jaundice. Fortunately, most people with this disease are expected to make a full recovery without suffering from any long-term complications.
8 Natural Treatments for Yellow Spots on the Skin

The best way to treat yellow spots on the skin is to identify the underlying cause, which is your doctor’s job. Sometimes, treatment isn’t even necessary because the underlying condition goes away on its own.
Just to give you a few helpful ideas, here are some ways to combat yellow spots or yellow skin without taking medical drugs or weird concoctions:
- Eat Iron-Packed Foods
- Drink 2-4 Cups of Coffee Daily
- Start Eating Papaya
- Shed the Extra Pounds
- Add Fiber-Rich Foods to Your Diet
- Stop Drinking Alcohol
- Try Spices and Herbs
- Get Adequate Rest
1. Eat Iron-Packed Foods
It’s common for people with liver disease to have anemia or a low red blood cell count. To eliminate anemia-related yellow spots or jaundice, you can raise your body’s iron level by taking iron supplements or eating foods that contain high levels of iron (recommended).
According to WebMD, the following are the top food sources of heme iron (35 milligrams/serving):
- Beef or chicken liver (3 ounces)
- Clams or mussels (3 ounces)
- Oysters (3 ounces)
Other good food sources of heme iron (2.1 milligrams/serving) include:
- Cooked beef (3 ounces)
- Canned sardines in oil (3 ounces)
Note: Heme iron is a form of iron that’s found only in seafood, fish, meat, and chicken (or other domestic fowls, like turkey and duck).
2. Drink 2-4 Cups of Coffee Daily
Drinking coffee every day benefits you in two ways:
- It reduces your risk of liver problems, such as fibrosis (scarring of healthy liver tissue) and cirrhosis (late-stage fibrosis).
- It slows the progression of liver disease in some instances.
Aim for 2-4 cups of coffee daily. In one study, the result has shown that drinking 2 cups of coffee a day lowers your risk of cirrhosis by 44%. It even gets better if you drink 4 cups a day since it reduces your risk by 65%. [5]
This health benefit doesn’t seem to be present in other caffeinated drinks, according to another study. [6] So, it’s better to stick with coffee.
Warning: Avoid drinking coffee if you have heart problems. Don’t drink it with other stimulants as well.
3. Start Eating Papaya
Papaya, also called pawpaw and fruit of the angels, is one of the richest sources of vitamin C, a potent antioxidant. One large papaya contains at least 235 milligrams of vitamin C, as well as calcium, potassium, and vitamin A.
Antioxidants are chemicals that combat the harmful effects of free radicals. These unstable atoms play a vital role in the development of serious diseases, such as liver disease and diabetes.
Studies have shown that fermented papaya is capable of reducing oxidative stress, which is an imbalance between free radicals and the antioxidants in the body. This is especially true in older adults and those suffering from mild hypothyroidism, liver disease, and prediabetes. [7]
4. Shed the Extra Pounds
Exercising or other physical activities can help keep your liver and gallbladder healthy. Harvard Health suggests aiming for a total of half an hour of exercise a day, most days of the week, to prevent gallstones. [8]
But what type of exercise is the best? There’s no single type of exercise that can prevent or treat medical conditions that cause yellowish skin discoloration. However, a study published in the journal Biomolecules offers a suggestion—aerobic exercise. [9]
The result of the same research study reveals that aerobic exercise could protect the liver from alcohol-related damage.
Examples of aerobic exercises include:
- Swimming
- Running or jogging
- Hiking
- Walking
- Kickboxing
- Cross-country skiing
- Outdoor biking
5. Add Fiber-Rich Foods to Your Diet
Foods that are rich in fiber—particularly soluble fiber—help the body to move bile from the liver and out of the body. Soluble fiber is better than insoluble fiber because it slows down food digestion by attracting and holding water and then changing into a gel-like substance during digestion.
The best sources of soluble fiber include:
- Apples
- Beans (dried)
- Barley
- Lentils
- Nuts
- Oat bran
- Rice bran
- Seeds
- Oats
- Potatoes
- Peas
- Strawberries
- Certain fruits and vegetables
6. Stop Drinking Alcohol
It’s easier said than done, but it’s an important step to take. If you’re struggling with alcoholism, talk to your doctor. Ask for recommendations regarding the best treatment program for alcoholism.
Although meds for treating alcoholism have been around for decades, only less than 10% of people use them, says Dr. Stephen Holt, who co-directs the Addiction Recovery Center at Yale-New Haven Hospital. [10]
One of these meds is naltrexone (brand name: ReVia or Vivitrol), which works by reducing your cravings for alcohol so that you can stay sober longer.
7. Try Spices and Herbs
Turmeric
Preliminary studies indicate that turmeric is effective against the hepatitis virus. For instance, in a 2010 study, scientists discovered that turmeric extract might help stop the replication of the hepatitis C virus. [11]
Milk Thistle
Milk thistle (Silybum marianum) is a flowering herb that’s native to the Mediterranean countries. It’s often used as an herbal remedy for high blood sugar, liver problems (like liver cirrhosis), and abnormally high cholesterol. This herb contains 65-80% silymarin, which has antioxidant, antiviral, and anti-inflammatory properties.
Burdock
Burdock (Arctium lappa) is an herb that’s used for different ailments, as well as for detoxification. According to a study published in the Current Therapeutic Research journal, burdock may help protect the liver from acetaminophen overdose. [12]
8. Get Adequate Rest
Getting rid of the yellowish discoloration of the skin depends heavily on treating or managing the underlying cause. When it comes to acute hepatitis, this usually means strict full bed rest. Depending on the hepatitis type, it may take 2-4 weeks (or possibly longer) for its symptoms to subside completely.
Conclusion – Yellow Spots on Skin: Causes and Treatments
So to recap our initial question: What causes yellow spots on skin? Also, how to treat yellow spots on skin? Hepatitis, liver problems, gallstones, atopic eczema, and thyroid problems, specifically hypothyroidism, are just some of the common causes of yellow spots on the skin or jaundice.
It’s essential to find out the exact cause of yellow skin discoloration to know the right treatment for your condition.
Natural therapies may include the use of herbs and spices, along with lifestyle and dietary modifications. Visit your doctor to ensure the cause of the yellow skin and to get an accurate diagnosis.
Try to incorporate some of the following8 natural treatments for getting rid of the yellow spots on your skin:
- Eat Iron-Packed Foods
- Drink 2-4 Cups of Coffee Daily
- Start Eating Papaya
- Shed the Extra Pounds
- Add Fiber-Rich Foods to Your Diet
- Stop Drinking Alcohol
- Try Spices and Herbs
- Get Adequate Rest
Related reading:
Pink Spots on Skin: Causes and Treatments
Uneven Skin Tone – How to Even It Out? 11 Tips

![Bleeding Pore on Nose [11 Possible Causes and Treatments] bleeding pore on nose](https://skincaregeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/04/bleeding-pore-on-nose-150x150.jpg)
![Bruise Itches [Causes and Treatments for an Itchy Bruise] bruise itches](https://skincaregeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/04/bruise-itches-150x150.jpg)
![Neutral Skin Tone Defined [and Best Colors for Neutral Skin] neutral skin tone](https://skincaregeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/neutral-skin-tone-150x150.png)