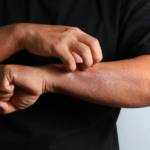
Accutane is a famous brand name for isotretinoin, which is a common medication for treating severe acne. You may have heard of stories indicating that it can treat other skin diseases too. Is Accutane good or bad for eczema?
Eczema is a possible side effect of using Accutane. Accutane should not be used as a possible treatment for eczema.
Isotretinoin, popularly known as Accutane, is marketed as an exclusive treatment for moderate to severe acne. It may be beneficial in treating other inflammatory skin diseases, but it should not be used to treat eczema. In fact, eczema is one of the side effects of Accutane.
Read on to learn more about whether Accutane is good or bad for eczema and other related information regarding Accutane.
Accutane Eczema [Is Accutane Good or Bad for Eczema?]
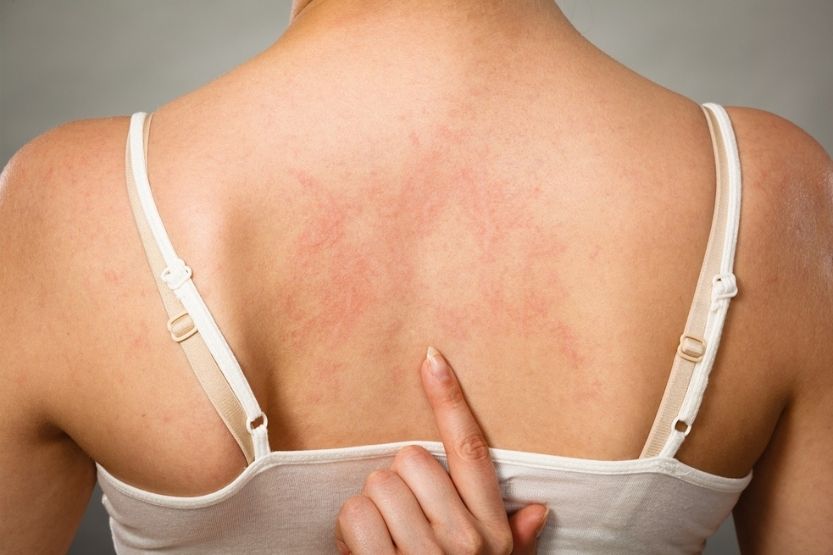

Isotretinoin, commonly known as Accutane, is exclusively marketed as a treatment for severe acne. It may help treat other skin diseases, but it may not be good for treating eczema. In fact, one of the side effects of Accutane is eczema.
One of the many side effects of Accutane includes itchy, flaking, peeling, and dry skin. Therefore, it can trigger redness of the face, a flare of eczema, and dermatitis. In short, no, Accutane is not good for eczema. Besides, manufacturers did not launch Accutane for that purpose.
Isotretinoin, also known as Accutane, is marketed as an exclusive treatment for acne. Users claim that it is beneficial in treating other inflammatory skin diseases. However, it may not be used to treat eczema. In fact, eczema is one of the side effects of Accutane.
Testimonials are indicating that users experienced acne breakouts in the first few months of their Accutane treatment. Then, these side effects disappeared, as well as their acne.
There were also acne patients who experienced the side effects right after completing the entire course of treatment.
Suffice it to say that Accutane is a highly effective prescription drug for the right acne patients under the right circumstances.
What Is Eczema?
Eczema or atopic dermatitis is a condition in which your skin gets extremely red and itchy. It is common among children and disappears as they grow older.
However, there are people — young and old alike — who experience extreme eczema too. At times, eczema is even accompanied by hay fever or asthma.
While acne, also sometimes referred to as pimple outbreak, manifests as spots occurring on oily skin, eczema, on the other hand, appears as itchy patches on dehydrated skin. But since eczema also occurs on the face, there may be times when it becomes difficult to tell them apart.
Similar to acne, there is no known permanent cure for eczema. Instead, some treatments can help you control it and prevent it from occurring.
How to Treat Eczema?
There are several ways to treat eczema. Here are some of them:
1. Creams
There are OTC creams or prescription creams that help repair damaged skin or at least control itching. In most cases, doctors prescribe a corticosteroid ointment or cream that patients can apply after taking a bath and moisturizing.
Make sure to follow the instructions given by your doctor. Otherwise, excessive use might cause thinning of the skin.
2. Prescription Drugs
If your skin has open sores, cracks, and/or bacterial infection, your physician will most likely prescribe an antibiotic. He may require you to take oral antibiotics for a certain period of time and then shift to antibiotic cream soon thereafter.
Your doctor may also require you to take oral corticosteroids for a short period of time. An example of this is prednisone. While this drug is effective, long-term use might result in serious side effects.
3. Dupilumab Injectable Biologic
The United States Food and Drug Administration (USFDA) has recently approved Dupixent treatment, an injectable biologic called Dupilumab that can treat severe eczema.
Studies proved the efficacy and safety of its use. However, it still does not have a long track record to strengthen claims of how effective it is.
4. Therapies
There are several therapies available for people with eczema. These include the following:
Wet Dressings Therapy
Wet Dressings therapy is an intensive treatment. This therapy involves wrapping the affected area of the skin with bandages infused with topical corticosteroids. This therapy requires a nurse’s expertise.
However, if you’re capable of doing this at home, you may do so with your physician’s approval.
Light Therapy
Physicians advise Light Therapy if your eczema doesn’t get better or it keeps reappearing even after treatment. Phototherapy is the simplest type of light therapy. Other types of light therapy include artificial ultraviolet A and narrowband ultraviolet B.
Counseling
Counseling is a recommended therapy for people with moderate to severe eczema. For this situation, eczema also affects self-esteem and mental health.
Relaxation, Behavior Modification, and Biofeedback
Relaxation, behavior modification, and biofeedback are good approaches for people who tend to habitually scratch.
Accutane & Its Benefits for People with Acne
Acne is a skin condition that has no permanent cure. Your acne may disappear today, but it may also reappear at any time. However, you can control it, and you can prevent it from getting worse.

People with moderate to severe acne may utilize Accutane. It is an oral medication that you can take once or twice a day, depending on your acne’s severity. Accutane or isotretinoin is a type of retinoid from a synthetic form of vitamin A.
Users can attest to its efficacy in clearing up acne completely, which other medications cannot do. Some even say that it is the most effective acne treatment of all.
Accutane shrinks the oil glands, or the sebaceous, in the skin. This successfully lessens the amount of oil produced, preventing it from clogging up the pores. Suffice it to say that it prevents pimples from forming and acne from progressing.
Unlike other medications considered maintenance drugs, there’s only a certain period of time to take Accutane. In most cases, one course of treatment is enough for a person with acne. In which case, you will have to take Accutane for a period of four to six months.
There are, however, cases when some patients have to take it for a longer period of time. This is to make the skin completely clear. After which, the dermatologist can prescribe topical acne medication to prevent acne from coming back.
Effects of Accutane for Acne Patients
Reports from dermatologists state that 70% of acne patients experience great results after taking Accutane. After finishing their treatment, acne has not reappeared, and it seems that their skin keeps getting clearer and clearer.
The other 30% of acne patients have stopped experiencing severe acne. Moreover, they only experienced mild acne. And they can treat those with topical medication. They can also opt for another course of Accutane treatment to achieve the desired results.
Accutane’s Side Effects
Accutane may be a valuable treatment for moderate to severe acne, but this drug also comes with side effects the patients should be aware of. Some of the side effects are severe that your doctor has to monitor you while under medication regularly.
This is why Accutane is a prescription drug and can never be an over-the-counter (OTC) drug.
Common Side Effects
Isotretinoin’s common side effects include the following:
- Joint pain;
- Photosensitivity;
- Nose bleeding;
- Chapped lips;
- Dry eyes, mouth and nose; and
- Itchy, flaking, peeling, and dry skin.
Here are some side effects that some people also experienced upon taking Accutane:
- Severe abdominal and/or chest pain;
- Headache;
- Fatigue;
- Blurred night vision; and
- Thinning of hair.
Some acne patients may also experience serious side effects. Note that these are rare occurrences but must not be taken lightly:
- Severe congenital disabilities in pregnant women;
- Elevated liver enzymes; and
- High blood triglycerides.
Taking Accutane is not a good idea if you’re pregnant or if you have other health conditions. As for women, you have to make sure that you don’t get pregnant while undergoing Accutane treatment.
Your physician can discuss these side effects with you in more detail. Also, if you experience side effects, make sure to contact your physician immediately.
Again, is Accutane good or bad for eczema? Some people who took Accutane experienced dry lips and eyes, dermatitis, and eczema. This can be referred to as “Accutane eczema.” Treating your eczema with Accutane is not good since Accutane and eczema are not good together.
Benefits of Accutane for People with Other Skin Conditions
Accutane is also beneficial for people with other skin conditions and may be prescribed off-label.
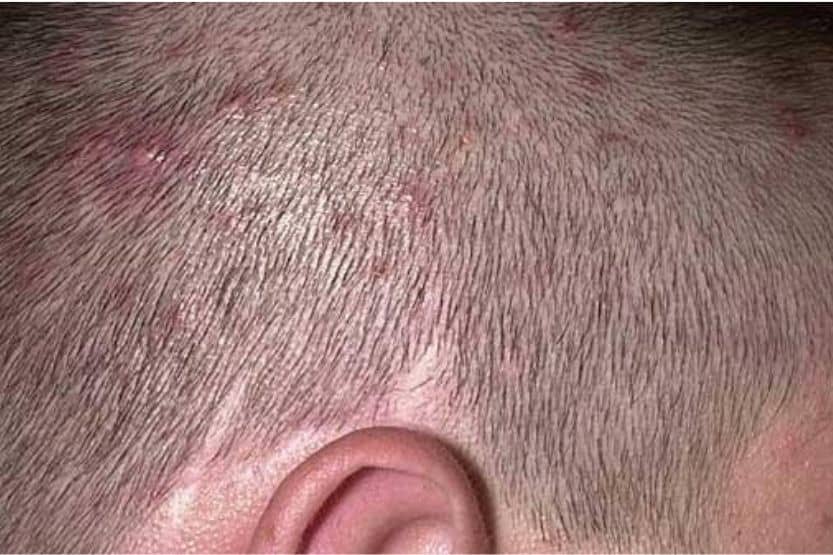
As for follicular conditions, these include:
- Scalp folliculitis (a disorder of the scalp’s hair follicles);
- Hidradenitis suppurativa (tiny lumps under the skin);
- Seborrhea (itchy, red rash and white scales); and
- Rosacea (redness of the skin).
Accutane also helps to relieve the following diseases:
- Prevention of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma;
- Extensive actinic keratoses;
- Sarcoidosis (presence of nodules in some organs);
- Grover disease (blisters located in the middle of the body; also known as Transient Acantholytic Dermatosis (TAD));
- Granuloma annulare (red bumps in a ring pattern); and
- Discoid lupus erythematosus.
Some physicians have used Accutane as an adjuvant in neuroblastoma. An adjuvant refers to the application done after initial cancer treatment to suppress a secondary tumor’s formation.
Ingredients of Accutane
1. Soybean Oil
Soybean oil is a kind of vegetable oil from Glycine max seeds. It has several uses and benefits, such as a food additive, insect repellent, and various medical uses. Unfortunately, treating eczema is not one of them because soy may cause eczema flares.
2. Hydrogenated Vegetable Oil
Hydrogenated vegetable oil comes from various edible oils extracted from several plants, such as soybeans, sunflowers, and olives. While vegetable oil may have health benefits, the process of hydrogenation produces trans fats that are harmful to our health.
Moreover, with soybeans’ presence in it, hydrogenated vegetable oil will most likely trigger a certain degree of inflammation.
3. Hydrogenated Soybean Oil Flakes
We know that soybean oil and hydrogenated vegetable oil are two ingredients that are bad for people with eczema. And hydrogenated soybean oil flakes are bad for eczema too.
4. Edetate Disodium
Edetate disodium is widely used in cosmetics, skincare products, and food and medicine, to name a few. It helps products maintain their quality.
5. Butylated Gydroxyanisole
Butylated hydroxyanisole has antioxidant properties and is a common ingredient for food and medicines. It is also an ingredient for cosmetics, animal feeds, food packaging, rubber, and even petroleum products.
The occurrence of eczema flares due to butylated hydroxyanisole is not commonly known. However, there have been reported cases of eczema appearing on fingers following oral administration.
6. Beeswax
Beeswax has been a popular ingredient in skincare products for centuries. Several studies have already been conducted on its effectiveness in healing skin problems. It helps calm, soothe, condition, and moisturize the skin.
Its antioxidant and inflammatory properties are perfect for people suffering from dry skin conditions such as eczema.
An ingredient, or two, in Accutane may be good for people with eczema. But it also contains ingredients that have adverse effects on them.
Conclusion – Accutane Eczema [Is Accutane Good or Bad for Eczema?]
Accutane, also known as isotretinoin, is a prescription drug exclusively for treating moderate to severe acne. It may help treat other types of skin diseases, but it is definitely not effective for treating eczema. In fact, eczema is one of the side effects of Accutane.
It contains ingredients beneficial for treating eczemas, such as beeswax and butylated hydroxyanisole. However, it also contains ingredients that trigger inflammation and eczema flares, such as soybean oil, hydrogenated vegetable oil, and hydrogenated soybean oil flakes.
So, to answer your question, is Accutane good or bad for eczema? The answer is, it is bad. Avoid considering using off-label treatments unless your doctor prescribes them.
Stick to treatments that are exclusive for people with eczema. They may have side effects, too but will definitely not worsen your skin condition.
Related reading:
Calamine Lotion for Eczema – Is it a Good Treatment?
Noxzema for Eczema [Is Noxzema Good or Bad for Eczema?]